The radio has been used for a long time, but I have never understood its principle. I heard it is very simple. Take some notes below.
1. Basic concepts
The radio is a small radio receiver, mainly used to receive radio broadcast programs and listen to radio transmitters. Let me first talk about the types of radios. According to the demodulation method and wavelength, they can be divided into the following categories:
Amplitude Modulation Radio (AM):
Long Wave Radio (LW, Long Wave)
Medium Wave Radio (MW, Medium Wave)
Short Wave Radio (SW, Short Wave)
FM radio (FM)
The radios we generally use are FM radios, and the band that FM radios can receive is generally 87.5-108MHz (pronounced as megahertz).
The slightly better ones can also receive AM. AM generally can receive the band 530-1710KHz (pronounced as kilohertz), this band is generally foreign broadcast stations.
For a deeper understanding, we first explain the two terms AM and FM:
AM: Amplitude Modulation
AM achieves the purpose of transmitting information by changing the amplitude of the output signal, adjusting the amplitude of the electromagnetic wave to change with the amplitude of the sound wave (the amplitude changes with time).
It can be represented by the following figure:
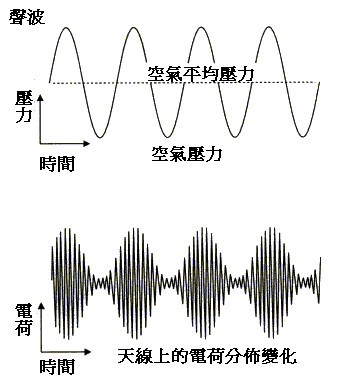
Amplitude modulation is usually referred to as medium wave, in the range of 503-1060KHz. Generally, medium wave broadcasting (MW: Medium Wave) uses Amplitude Modulation (Amplitude Modulation), so everyone slowly uses AM to represent MW. In fact, MW is just a kind of broadcast using AM modulation. The modulation method used in international shortwave broadcasting at high frequencies (3-30MHz) is also AM, and even higher frequency aviation navigation communications (116-136MHz) than FM broadcasting also uses AM.
FM: Frequency Modulation
FM is a modulation method that uses the instantaneous frequency change of the carrier to express information. Adjust the frequency of electromagnetic waves to change with the amplitude of sound waves (frequency changes with time).
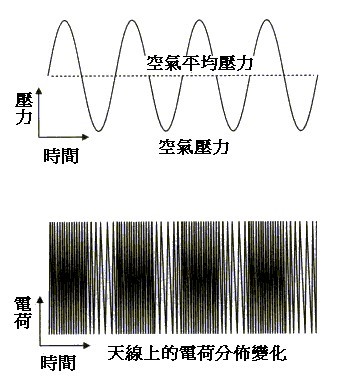
We are accustomed to using FM to refer to general FM broadcasting (76-108MHz, 87.5-108MHz in our country, 76-90MHz in Japan, MHz is read as megahertz), in fact FM is just a modulation method, even in the shortwave range Between 27-30MHz inside, as the band for amateur radio, space, satellite communication applications, there are also frequency modulation (FM) methods.
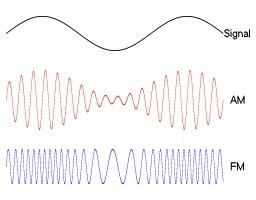
The following figure shows the difference between the two:
The top is the sound wave signal. When the sound wave signal is strengthened, AM will increase the amplitude, FM will strengthen the frequency, and vice versa.
2. Working principle
This part mainly involves the following concepts: acoustic waves, electromagnetic waves, and carrier waves.
Sound wave: The sound that can be heard by the human ear is called sound wave, and the frequency range of the sound wave that can be heard by the human ear is 20Hz-20,000Hz. The sound wave propagates in the air attenuation greatly, and the transmission distance is very short.
Radio waves: The frequency of radio waves is much higher than the audible frequency range of human ears, and the propagation medium is electromagnetic fields. Long transmission distance.
Carrier wave: In order to make the sound travel farther, people let the sound wave signal ride on the "fast train" of radio wave signals. In professional terms, we call this "fast train" the carrier wave. Then there is another problem that needs us to consider. If we take this "express train", there are usually two ways that can be used, one is amplitude modulation (AM) and the other is frequency modulation (FM).
Broadcasting is generally sent out by various stations. We use our own radio to receive the signal from the station, and then convert it to output sound through the speaker. Let's talk about sending and receiving separately:
send:
The broadcaster is responsible for generating sound waves (speech changes the pressure (density) in the air), which are converted into audio electric signals by electro-acoustic devices, and amplified by the audio amplifier, and the oscillator generates high-frequency equal-amplitude oscillation signals. The modulator makes the high-frequency constant-amplitude oscillation signal modulated by the audio signal, and the modulated high-frequency oscillation signal is amplified and sent to the transmitting antenna, where it is converted into radio waves and radiated out.
receive:
The reception of wireless broadcasting is realized by the radio. The receiving antenna of the radio receives the air wave, the tuning circuit selects the signal of the required frequency, and the high frequency signal of the detector is restored to the audio signal (ie demodulation), which is obtained after demodulation. The audio signal is amplified to obtain sufficient driving power, and finally the broadcast content is restored through electro-acoustic conversion.
Our other product:


















