The radio frequency amplifier is basically the positive feedback system in our radio frequency system, which is generally located on the transmission link. Due to the consideration of link attenuation of wireless transmission, the transmitter needs to radiate enough power to obtain a relatively long communication distance. Therefore, the radio frequency amplifier is mainly responsible for amplifying the power to a large enough level and then feeding it to the antenna for radiation out. It is the core device in the communication system.
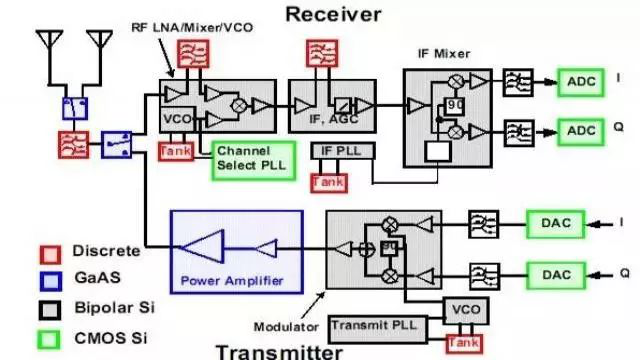
So for such an important device, what are the main types of RF amplifiers?
1) Classification from working frequency band
Classified by working frequency band, it can be divided into narrowband radio frequency power amplifier and broadband radio frequency power amplifier. Narrowband RF power amplifiers generally use a frequency selective network as a load circuit, such as an LC resonant circuit. Broadband RF power amplifiers do not use a frequency-selective network as the load loop, but use a transmission line with a wide frequency response as the load.
2) Classification from the nature of the matching network
According to the nature of the matching network, power amplifiers can be divided into non-resonant power amplifiers and resonant power amplifiers. The matching network of a non-resonant power amplifier is a non-resonant system, such as a high-frequency transformer, a transmission line transformer, and other non-resonant systems, and its load properties are purely resistive. The matching network of the resonant power amplifier is a resonant system, and its load properties show reactive properties.
3) Classified by current conduction angle
According to the current conduction angle, RF power amplifiers can be classified into Class A, Class AB, Class B, Class C, Class D, Class E, etc. In the classification of amplifiers, we often talk about amplifiers of class A to E divided by conduction angle. The output power and efficiency of the Class C working state are the highest among these working states, and most of the amplifiers used for radio frequency work in C (C).
The classification of amplifiers is already so complicated, it can be seen that the main performance indicators are certainly not simple, in fact it is the same.
The main indicators of the amplifier are as follows:
1. Operating frequency range
Generally speaking, it refers to the linear operating frequency range of the amplifier. If the frequency starts from DC, the amplifier is considered to be a DC amplifier.
2. Gain
Working gain is the main indicator to measure the amplifier's amplification capability. The definition of gain is the ratio of the power delivered to the load from the output port of the amplifier to the power actually delivered to the input port of the amplifier from the signal source.
Gain flatness refers to the range of amplifier gain in the entire operating frequency band at a certain temperature, and it is also a main indicator of the amplifier.
3. Output power and 1dB compression point (P1dB)
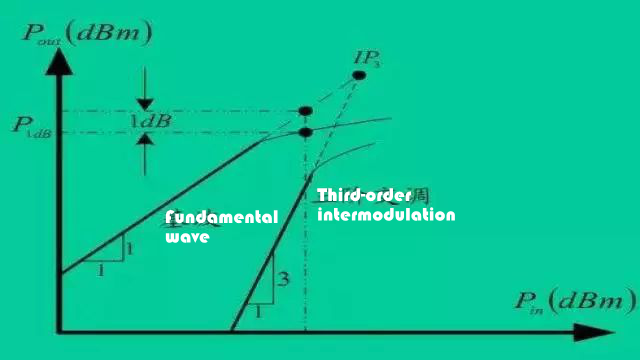
Refer to the figure above, when the input power exceeds a certain value, the gain of the transistor begins to decrease, and the final result is that the output power reaches saturation. When the gain of the amplifier deviates from a constant or is 1dB lower than other small signal gains, this point is the famous 1dB compression point (P1dB). Generally speaking, the power capacity of an amplifier is expressed by the 1dB compression point.
4. Efficiency
Since the power amplifier is a power component, it needs to consume power supply current. Therefore, the efficiency of the power amplifier is extremely important to the efficiency of the entire system. Power efficiency is the ratio of the RF output power of the power amplifier to the DC power supplied to the transistor. ηp=RF output power/DC input power
5. Intermodulation Distortion (IMD)
Intermodulation distortion refers to the mixed component produced by two or more input signals with different frequencies passing through a power amplifier. This is due to the non-linear nature of the power amplifier. Among them, because the third-order intermodulation product is very close to the fundamental wave signal and has the greatest impact, the most important consideration among the intermodulation products is the third-order intermodulation. The lower the third-order intermodulation product, the better.
6. Third-order intermodulation cut-off point (IP3)
The intersection of the fundamental signal output power extension line and the third-order intermodulation extension line in Figure 2 is called the third-order intermodulation cut-off point, which is represented by the symbol IP3. IP3 is also an important indicator of power amplifier nonlinearity. When the output power is constant, the greater the output power at the third-order intercept point, the better the linearity of the power amplifier.
7. Dynamic range
The dynamic range of a power amplifier generally refers to the difference between the smallest detectable signal and the maximum input power in the linear working area. Naturally, this value must be as large as possible.
8. Harmonic distortion
When the input signal increases to a certain level, the power amplifier will generate a series of harmonics due to the work in the nonlinear region. For high-power amplifier systems, it is generally necessary to use filters to reduce the harmonics below 60dBc.
9. Input/output standing wave ratio
This is also a very important indicator, indicating the degree of matching between the power amplifier and the entire system. The deterioration of the input/output ratio will result in the fluctuation of the system's gain and the deterioration of the group delay. However, it is more difficult to design a power amplifier with a high standing wave ratio. In general systems, it is necessary to require the input standing wave ratio of the power amplifier to be lower than 2:1.
Our other product:

















