
1. TRS interface
Most people may not know what it is at first hearing, but as long as you put the real thing in front of you, everyone will know what it is. In fact, the most common thing we see in daily life is the TRS connector. Its connector appearance is cylindrical, usually in three sizes: 1/4" (6.3mm), 1/8" (3.5mm), 3/32" (2.5mm) ), our most common is the 3.5mm size connector.
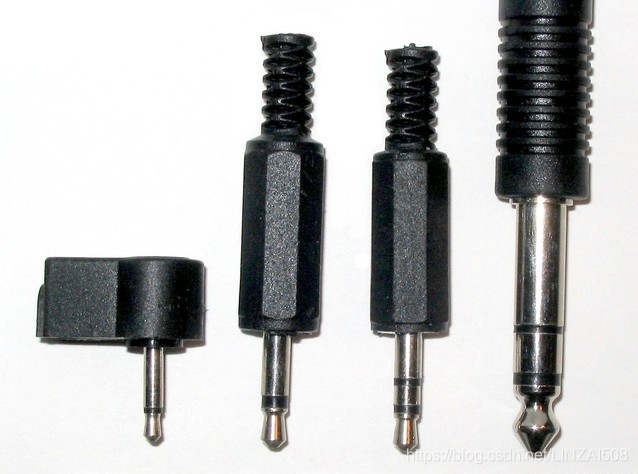

The 2.5mm TRS connector used to be popular on mobile phone headsets, but now it is rare. The headset interface is basically dominated by the 3.5mm interface. The 6.3mm connector is more common in many professional equipment and high-end headsets, but now many high-end headsets have gradually begun to switch to 3.5mm connectors. The meaning of TRS is Tip (signal), Ring (signal), Sleep (ground), which respectively represent the three contacts of this joint. What we see is three sections of metal pillars separated by two sections of insulating material. Therefore, 3.5mm connectors and 6.3mm connectors are also called "small three cores" and "big three cores".
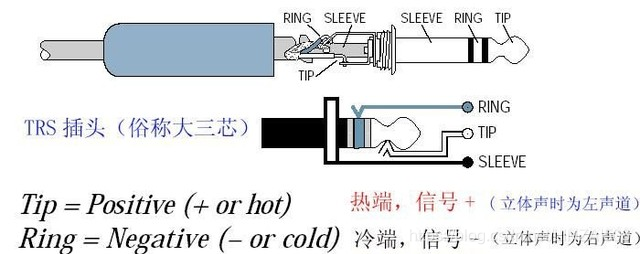
2. The structure of the "big three core"
The TRS interface is a round hole, the inside of which corresponds to the connector, and there are also three contacts, which are also separated by insulating materials. Some people say there are no four-pin plugs? That's right, the four-pin plug we see on headphones or walkmans, the extra core is used to transmit voice signals or control signals. In addition, there is a four-core 3.5mm plug for headphones that is used to transmit balanced signals. The 6.3mm "big three-pin" plug can be used to transmit balanced signals or unbalanced stereo signals, that is to say, it can transmit balanced signals like the XLR balanced interface we will talk about later, but the cost of making such a balanced cable is relatively high. High, so it is generally only used on high-end professional audio equipment.
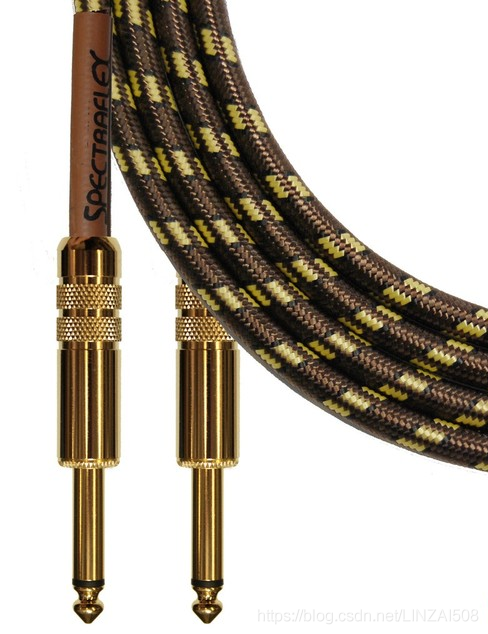

3. Two-core 6.3mm TRS electric guitar cable
Of course, since cores can be added, cores can also be reduced. The two-core TRS connector can be used to transmit unbalanced mono audio signals. For example, the cable for electric guitars is a two-core TRS cable. Therefore, from the appearance of the TRS interface, we do not know whether it supports balanced transmission; from the core count alone, we cannot be sure whether the TRS connector with four cores and above supports balanced transmission. The specific situation depends on the equipment.
4. RCA interface
It is also very common in our daily life, and it is basically available in equipment such as speakers, TVs, power amplifiers, and DVD players. It is named after the English abbreviation of Radio Corporation of America (Radio Corporation of America). In the 1940s, the company introduced this interface to the market and used it to connect phonographs and speakers. Therefore, it is also called in Europe PHONO interface. The connector we are more familiar with is called "lotus head".
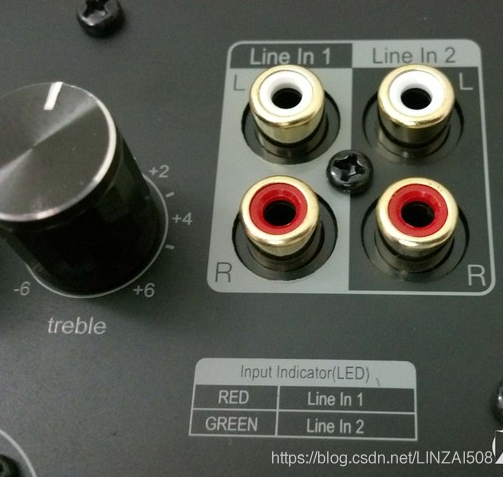

RCA connector of "lotus head"
The RCA interface uses the coaxial [coaxial definition as shown in the figure below] to transmit signals. The central axis is used to transmit signals, and the contact layer on the outer edge is used for grounding. Each RCA cable is responsible for transmitting the audio signal of one channel. Therefore, you can use the number of RCA cables that match the actual needs of the channel. For example, to set up two-channel stereo, two RCA cables are needed.
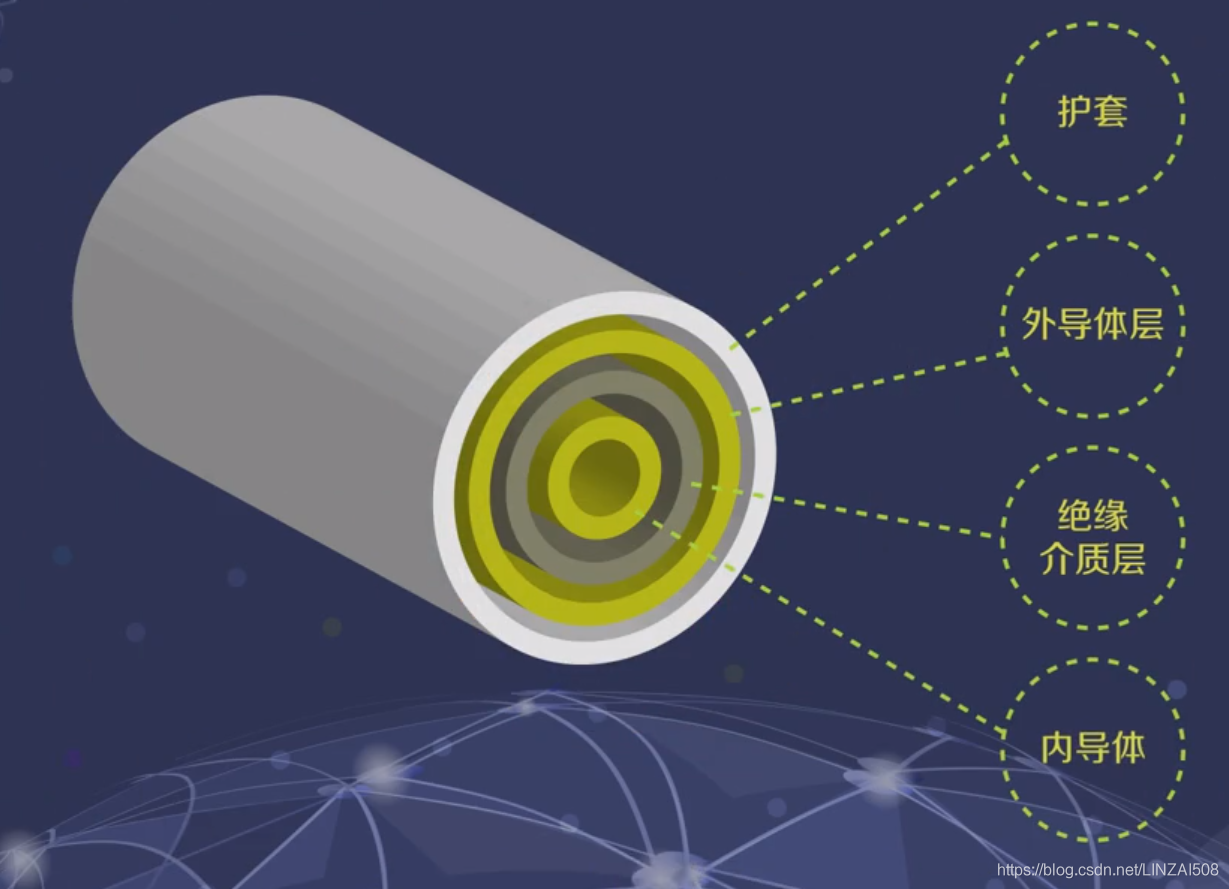
5. Coaxial definition
SPDIF's COAXIAL (coaxial)

1) Coaxial digital audio interface output
The coaxial digital audio interface output is the abbreviation of (Sony/Philips Digital InterFace) SONY and PHILIPS home digital audio interface. It is a specification that specifies the transmission of digital signals. It can transmit a variety of signals, and can transmit LPCM streams and Dolby Digital, DTS, Surround sound compression audio signals such as AC-3.
SPDIF is divided into coaxial and optical fiber from the transmission medium. In fact, the signals that they can transmit are the same, but the carrier is different, and the interface and connection appearance are also different. As long as the electrical signal is converted into an optical signal, it can be transmitted by optical fiber (Optical). Optical signal transmission is a popular trend in the future, and its main advantage is that it does not need to consider the interface level and impedance issues, the interface is flexible and the anti-interference ability is stronger.
2) Coaxial audio interface (Coaxial)
Coaxial audio interface (Coaxial), the standard is SPDIF (Sony / Philips Digital InterFace), which is jointly formulated by Sony and Philips. Coaxial is marked on the back panel of audio-visual equipment, mainly to provide digital audio signal transmission . Its connectors are divided into RCA and BNC.
Coaxial audio is an audio interface that also has input and output functions. Unlike the previous audio interface, it integrates the interface of the microphone (input interface) and the interface of the headset or audio (output interface).
Coaxial audio interface (Coaxial)
SPDIF fiber
Optical fiber [interface where the frame is located]
6. Square and round fiber connectors
The English name of the optical fiber interface is TOSLINK, which comes from the technical standards formulated by Toshiba (TOSHIBA), and the equipment is generally marked as "Optical". Its physical interface is divided into two types, one is a standard square head, and the other is a round head similar to the 3.5mm TRS connector commonly found on portable devices. Since it transmits digital signals in the form of light pulses, it is the fastest transmission speed from a technical point of view.
The optical fiber connection can achieve electrical isolation, prevent digital noise from being transmitted through the ground wire, and help improve the signal-to-noise ratio of the DAC. However, since it needs a light emitting port and a receiving port, and the photoelectric conversion of these two ports requires photodiodes, there can be no close contact between the optical fiber and the photodiode, which will produce digital jitter-like distortion, and this distortion is superimposed of. Coupled with the distortion in the photoelectric conversion process, it is much worse than the coaxial in terms of digital jitter. Therefore, now the optical fiber interface has gradually faded out of people's field of vision.
7. XLR interface of AEX/EBU interface
Also known as "Cannon mouth", this is because the Cannon Electric company founded by James H. Cannon is its original manufacturer. Their earliest product was the "cannon X" series. Later, the improved product added a locking device (Latch), so an "L" was added after the "X"; later, a rubber seal was added around the metal contacts of the joint. (Rubber compound), so an "R" is added after the "L". People put the three capital letters together and called this connector "XLR connector".
Common three-core XLR interface
Some amps will provide a four-core balanced XLR headphone jack
The XLR plugs we usually see are 3-pin, of course, there are also 2-pin, 4-pin, 5-pin, and 6-pin. For example, on some high-end headphone cables, we will also see four-pin XLR balanced connectors. The XLR interface is the same as the "big three-core" TRS interface, which can be used to transmit audio balanced signals. Here we briefly talk about balanced signals and unbalanced signals. After the sound wave is converted into an electrical signal, if it is directly transmitted, it is an unbalanced signal. If the original signal is inverted by 180 degrees, and then the original signal and the inverted signal are transmitted at the same time, it is a balanced signal. Balanced transmission is to use the principle of phase cancellation to minimize other interference during audio signal transmission. Of course, the XLR interface is the same as the "big three-core" TRS interface, which can transmit unbalanced signals, so we can't see what kind of signal it is transmitting from the interface.
**In terms of digital audio interface, we are actually talking more about transmission protocols or standards. From the physical appearance of the interface, it is difficult to tell which type of interface it is. Let us first talk about AES/EBU. **
AES/EBU is the abbreviation of Audio Engineering Society/European Broadcast Union, and it is the more popular professional digital audio standard. It is a serial bit transmission protocol based on a single twisted pair to transmit digital audio data. Data can be transmitted over a distance of up to 100 meters without equalization, and if equalized, it can be transmitted over longer distances.
The most common AES/EBU physical interface with three-core XLR interface
AES/EBU provides two channels of audio data (up to 24-bit quantization), the channels are automatically timed and self-synchronized. It also provides the method of transmission control and the representation of status information (channel status bit) and some error detection capabilities. Its clock information is controlled by the transmitting end and comes from the bit stream of AES/EBU. Its three standard sampling rates are 32kHz, 44.1kHz, and 48kHz. Of course, many interfaces can work at other different sampling rates.
There are many physical interfaces of AES/EBU, the most common is the three-core XLR interface, used for balanced or differential connection; in addition, there are audio coaxial interfaces using RCA plugs to be discussed later, used for single-ended unbalanced Connect; and use fiber optic connectors to make optical connections.
S/PDIF is the abbreviation of Sony/Philips Digital Interconnect Format, which is a civilian digital audio interface protocol developed by Sony and Philips. Because of its widespread adoption, it has become the de facto standard for civilian digital audio formats. S/PDIF and AES/EBU have slightly different structures. Audio information occupies the same position in the data stream, making the two formats compatible in principle. In some cases, AES/EBU professional equipment and S/PDIF user equipment can be directly connected, but this approach is not recommended because there are very important differences in electrical specifications and channel status bits. When using mixed protocols May have unpredictable consequences.
S/PDIF interface with RCA coaxial and optical interface
S/PDIF interface
There are generally three types, one is RCA coaxial interface, the other is BNC coaxial interface, and the other is TOSLINK optical interface. In international standards, S/PDIF requires a BNC interface 75 ohm cable for transmission. However, for various reasons, many manufacturers frequently use RCA interfaces or even 3.5mm small stereo interfaces for S/PDIF transmission. Over time, RCA and 3.5mm interfaces are Become a "civil standard." We will talk about the coaxial interface and the optical interface in detail later.
There are two types of coaxial interfaces, one is RCA coaxial interface and the other is BNC coaxial interface. The appearance of the former is no different from the analog RCA interface, while the latter is a bit similar to the signal interface we commonly use on TV sets, and has a locking design. The coaxial cable connector has two concentric conductors, the conductor and the shield share the same axis, and the impedance of the line is 75 ohms.
Coaxial cable with BNC coaxial interface
The coaxial transmission impedance is constant and the transmission bandwidth is high, so the audio quality can be guaranteed. However, although the appearance of the RCA coaxial interface is the same as the RCA analog interface, it is best not to mix the cables. Because the RCA coaxial cable has a fixed 75 ohm impedance, mixed cables will cause unstable sound transmission and degrade the sound quality.
The English name of the optical fiber interface is TOSLINK, which comes from the technical standards formulated by Toshiba (TOSHIBA), and the equipment is generally marked as "Optical". Its physical interface is divided into two types, one is a standard square head, and the other is a round head similar to the 3.5mm TRS connector commonly found on portable devices. Since it transmits digital signals in the form of light pulses, it is the fastest transmission speed from a technical point of view.
Square and round fiber optic connectors
The optical fiber connection can achieve electrical isolation, prevent digital noise from being transmitted through the ground wire, and help improve the signal-to-noise ratio of the DAC. However, since it needs a light emitting port and a receiving port, and the photoelectric conversion of these two ports requires photodiodes, there can be no close contact between the optical fiber and the photodiode, which will produce digital jitter-like distortion, and this distortion is superimposed of. Coupled with the distortion in the photoelectric conversion process, it is much worse than the coaxial in terms of digital jitter. Therefore, now the optical fiber interface has gradually faded out of people's field of vision.
Our other product:






















