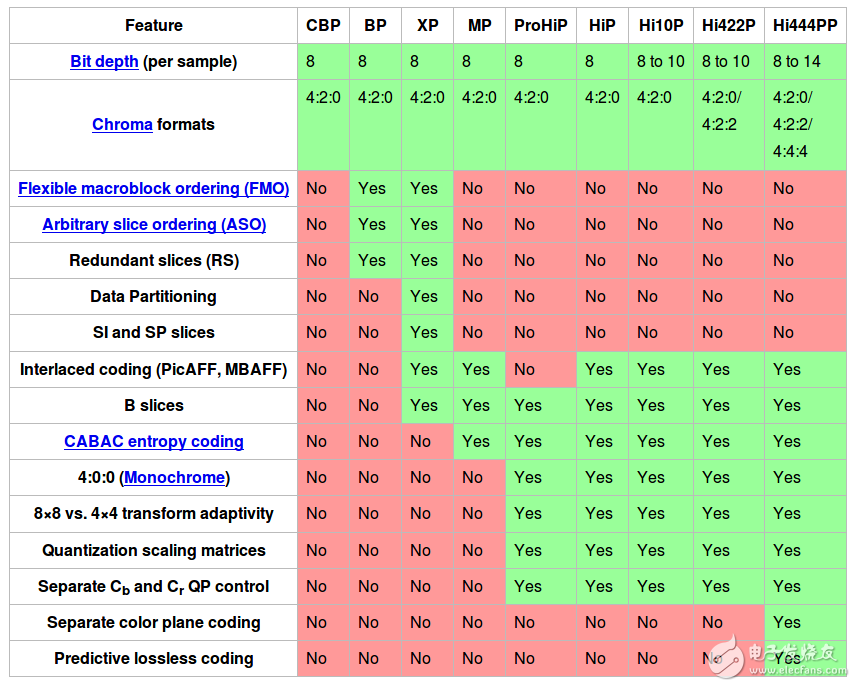
Feature support in particular profiles
1. level
When the term is used in the standard, "level" is a specified set of constraints that indicate the degree of decoder performance required by the profile. For example, the support level in the configuration file specifies the maximum image resolution, frame rate, and bit rate that the decoder can use. A decoder that conforms to a given level must be able to decode all bitstreams coded for that level and all lower levels.
Levels with maximum property values
The maximum bit rate of High Profile is 1.25 times of Constrained Baseline, Baseline, Extended and Main Profiles; Hi10P is 3 times, Hi422P/Hi444PP is 4 times.
The number of luminance samples is 16×16 = 256 times the number of macroblocks (and the number of luminance samples per second is 256 times the number of macroblocks per second).
2. Decoded picture buffer
H.264/AVC encoders use previously encoded pictures to provide predictions of sample values in other pictures. This allows the encoder to make effective decisions on the best way to encode a given image. At the decoder, these pictures are stored in a virtual decoded picture buffer (DPB). The maximum capacity of DPB, in units of frames (or field pairs), as shown in the brackets in the right column of the above table, can be calculated as follows:
DpbCapacity = min(floor(MaxDpbMbs /(PicWidthInMbs * FrameHeightInMbs)), 16)
Where MaxDpbMbs is the constant value provided in the following table as a function of the level number, and PicWidthInMbs and FrameHeightInMbs are the picture width and frame height of the encoded video data, expressed in units of macroblocks (rounded to an integer value and cropped) and macroblock pairing ( If applicable)). This formula is specified in sections A.3.1.h and A.3.2.f of the 2017 edition of the standard.
Because H.264 encoding and decoding require a large amount of computing power in certain types of arithmetic operations, software implementations running on general-purpose CPUs generally consume less power. However, the latest quad-core general-purpose x86 CPU has enough computing power to perform real-time SD and HD encoding. The compression efficiency depends on the implementation of the video algorithm, not on whether it is implemented using hardware or software. Therefore, the difference between hardware-based and software-based implementations depends more on power efficiency, flexibility, and cost. In order to improve power efficiency and reduce the hardware form factor, dedicated hardware can be used for the complete encoding or decoding process, or for acceleration assistance in the CPU control environment.
It is known that CPU-based solutions are more flexible, especially when encoding must be performed in multiple formats, multiple bitrates and resolutions (multi-screen video) at the same time, and may have additional features such as container format support, advanced integrated advertising features, etc. . CPU-based software solutions usually make it easier to load balance multiple concurrent encoding sessions within the same CPU.
The second-generation Intel "Sandy Bridge" Core i3/i5/i7 processor launched at CES (Consumer Electronics Show) in January 2011 provides an on-chip hardware full HD H.264 encoder called Intel Quick Sync Video.
The hardware H.264 encoder can be an ASIC or FPGA.
ASIC encoders with H.264 encoder functions are available from many different semiconductor companies, but the core designs used in ASICs are usually obtained from a few companies such as Chips & Media, Allegro DVT, On2 (formerly Hantro, acquired by Google) License, Imagination Technologies, NGCodec. Some companies have both FPGA and ASIC products.
Texas Instruments (TI) produces a series of ARM + DSP cores that execute 1080p DSP H.264 BP encoding at 30fps. This allows the flexibility of the codec (which is implemented as highly optimized DSP code) while being more efficient than software on general-purpose CPUs.
2. license
See also: Microsoft Corp. v. Motorola Inc. and Qualcomm Inc. v. Broadcom Corp.
In countries that maintain software algorithm patents, suppliers and commercial users of products using H.264/AVC are expected to pay patent licensing fees for the patented technology used in their products. This also applies to the baseline profile.
A private organization called MPEG LA, which is not affiliated with the MPEG standardization organization, manages the patent licenses applicable to the standard, as well as the patent pool of the MPEG-2 Part 1 system, MPEG-2 Part 2 Video, and MPEG-4 Part 1. 2 part video, HEVC, MPEG-DASH and other technologies. The US MPEG LA H.264 patent will last until at least 2027.
On August 26, 2010, MPEG LA announced that it would never charge royalties for free H.264-encoded Internet video for end users. All other royalties still exist, such as royalties on products that decode and encode H.264 video and operators of free TV and subscription channels. The license terms are updated in blocks of 5 years.
The actual status of the legal patent expired at the end of 2018, with a total of 123 pages.
In 2005, Qualcomm, the assignee of U.S. Patent 5,452,104 and U.S. Patent 5,576,767, sued Broadcom in the U.S. District Court, claiming that Broadcom infringed these two patents by manufacturing products that conform to the H.264 video compression standard. In 2007, the District Court ruled that the patents could not be enforced because Qualcomm failed to disclose these patents to JVT before the H.264 standard was released in May 2003. In December 2008, the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit confirmed the district court’s unenforceable order of patents, but issued instructions to the district court to limit the unenforceable scope to products that comply with the H.264 standard.
External links
Our other product:

















