A mobile phone that can support phone calls, text messages, network services, and APP applications usually contains five parts: radio frequency, baseband, power management, peripherals, and software.
Radio frequency: generally the part of information sending and receiving; baseband: generally the part of information processing; power management: generally the power-saving part. Since mobile phones are devices with limited energy, power management is very important; peripherals: generally include LCD , Keyboard, chassis, etc.; software: generally includes systems, drivers, middleware, and applications.
In the mobile phone terminal, the most important core is the radio frequency chip and the baseband chip. The radio frequency chip is responsible for radio frequency transceiver, frequency synthesis, power amplification; the baseband chip is responsible for signal processing and protocol processing. So what is the relationship between the RF chip and the baseband chip?
The relationship between RF chip and baseband chip
Radio frequency (Radio Frenquency) and baseband (Base Band) are both literally translated from English. Among them, the earliest application of radio frequency is Radio-radio broadcasting (FM/AM), which is still the most classic application of radio frequency technology and even the radio field.
The baseband is the signal with the center point of the band at 0Hz, so the baseband is the most basic signal. Some people also call the baseband "unmodulated signal". Once this concept was correct, for example, AM is a modulated signal (no modulation is required, and the content can be read through sound components after receiving).
But for the modern communication field, baseband signals usually refer to digitally modulated signals with the center of the spectrum at 0 Hz. And there is no clear concept that the baseband must be analog or digital, it all depends on the specific implementation mechanism.
Closer to home, baseband chips can be considered to include modems, but not only modems, but also channel codec, source codec, and some signaling processing. The RF chip can be regarded as the simplest up-conversion and down-conversion of baseband modulated signals.
The so-called modulation is the project of modulating the signal to be transmitted on the carrier through a certain rule and then sending it out through the RF Transceiver. Demodulation is the opposite process.
Working principle and circuit analysis
Radio frequency is abbreviated as RF. Radio frequency is radio frequency current, which is a kind of high-frequency alternating current electromagnetic wave. It is the abbreviation of Radio Frequency, which means the electromagnetic frequency that can be radiated into space. The frequency range is between 300KHz and 300GHz. The alternating current that changes less than 1,000 times per second is called low-frequency current, and the one that changes more than 10,000 times is called high-frequency current. Radio frequency is such a high-frequency current. High frequency (greater than 10K); radio frequency (300K-300G) is the higher frequency band of high frequency; microwave frequency band (300M-300G) is the higher frequency band of radio frequency. Radio frequency technology is widely used in the field of wireless communication, and the cable television system uses radio frequency transmission.
The radio frequency chip refers to an electronic component that converts radio signal communication into a certain radio signal waveform and sends it out through antenna resonance. It includes a power amplifier, a low noise amplifier and an antenna switch. The radio frequency chip architecture includes two parts: receiving channel and transmitting channel.
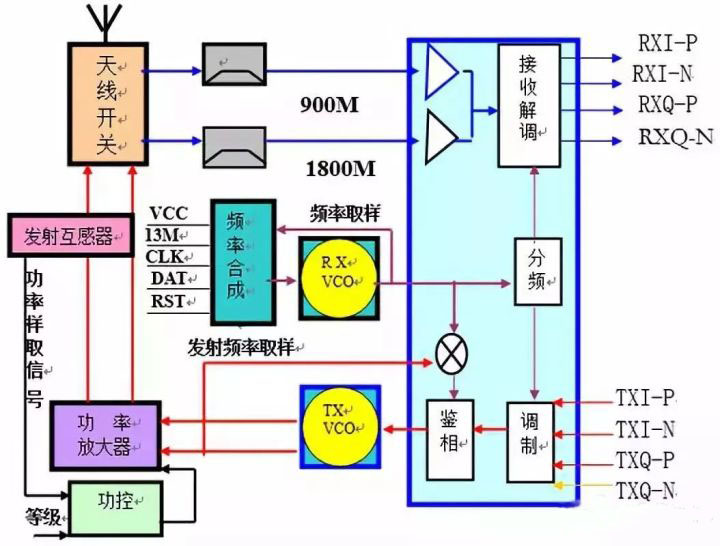
Block diagram of transmitting circuit
2. The function and role of each component
1) Transmitting modulator: Structure: Transmitting modulator is inside the intermediate frequency, which is equivalent to MOD in broadband network. Function: When transmitting, the transmission baseband information (TXI-P; TXI-N; TXQ-P; TXQ-N) processed by the logic circuit and the local oscillator signal are modulated into the transmission intermediate frequency.
2) Transmit Voltage Controlled Oscillator (TX-VCO): Structure: Transmitting Voltage Controlled Oscillator is a capacitor three-point oscillator circuit whose output frequency is controlled by voltage; it is integrated into a small circuit board during production and has five pins: Power supply pin, ground pin, output pin, control pin, 900M/1800M frequency switching pin. When there is a suitable working voltage, it will oscillate to generate a corresponding frequency signal.
Function: Transmit the IF signal modulated by the IF internal modulator into the 890M-915M (GSM) frequency signal that the base station can receive.
Principle: As we all know, the base station can only receive the frequency signal of 890M-915M (GSM), while the intermediate frequency signal modulated by the intermediate frequency modulator (such as Samsung IF signal 135M) cannot be received by the base station. Therefore, TX-VCO must be used to transmit the intermediate frequency signal The frequency becomes 890M-915M (GSM) frequency signal.
When transmitting, the power supply part sends out 3VTX voltage to make TX-VCO work, and generate the frequency signal of 890M-915M (GSM) in two ways: a), the sample is sent back to the IF, mixed with the local oscillator signal to produce one and the transmission IF The equal transmission frequency discrimination signal is sent to the phase detector to compare with the transmission intermediate frequency; if the TX-VCO oscillation frequency does not match the working channel of the mobile phone, the phase detector will generate a 1-4V jump voltage (with AC transmission DC voltage of information) to control the capacitance of the internal varactor in TX-VCO to achieve the purpose of adjusting frequency accuracy. b). After being amplified by the power amplifier, the antenna is converted into electromagnetic wave radiation.
It can be seen from the above that the frequency is generated by the TX-VCO until the sample is sent back to the IF, and then the voltage is generated to control the TX-VCO work; it just forms a closed loop and controls the frequency phase, so this circuit is also called transmit phase lock Ring circuit.
3) Power amplifier (power amplifier): Structure: The current mobile phone power amplifier is a dual-frequency power amplifier (900M power amplifier and 1800M power amplifier integrated), divided into vinyl power amplifier and iron case power amplifier; different models of power amplifiers cannot be interchanged.
Function: Amplify the frequency signal oscillated by TX-VCO to obtain sufficient power current, which is transformed into electromagnetic wave and radiated by the antenna.
It is worth noting that the power amplifier amplifies the amplitude of the transmitted frequency signal, and cannot amplify its frequency.
The working conditions of the power amplifier: a), working voltage (VCC): the power supply of the mobile phone power amplifier is directly provided by the battery (3.6V); b), the ground terminal (GND): the current forms a loop; c), the dual-frequency power conversion signal ( BANDSEL): control the power amplifier to work at 900M or 1800M; d), power control signal (PAC): control the amplification of the power amplifier (working current); e), input signal (IN); output signal (OUT). 4) Transmitting transformer: Structure: Two coils with equal wire diameter and number of turns are close to each other, and are composed of mutual inductance principle. Function: Send the power amplifier transmit power current sampling to the power control. Principle: When the transmitting power current of the power amplifier passes through the transmitting transformer during transmission, a current of the same magnitude as the power current is induced in its secondary, which is detected (high frequency rectification) and sent to the power control.
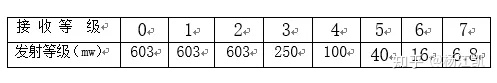
5) Power level signal: The so-called power level means that engineers divide the received signal into eight levels when programming the mobile phone. Each receiving level corresponds to the first level of transmission power (as shown in the table below). When the mobile phone is working, the CPU is based on the received signal. The strength is used to judge the distance between the mobile phone and the base station, and send an appropriate transmission level signal to determine the amplification of the power amplifier (that is, when the reception is strong, the transmission is weak).
Attached power rating table:
6) Controlador de potencia (control de potencia): estructura: un amplificador de comparación operacional. Función: Compare la señal de muestreo de corriente de potencia transmitida con la señal de nivel de potencia para obtener una señal de voltaje adecuada para controlar la amplificación del amplificador de potencia. Principio: Cuando la corriente de potencia pasa a través del transformador de transmisión durante la transmisión, la corriente inducida en su secundario se detecta (rectificación de alta frecuencia) y se envía al control de potencia; al mismo tiempo, la señal de nivel de potencia preestablecido también se envía al control de potencia durante la programación; dos Después de comparar estas señales internamente, se genera una señal de voltaje para controlar la amplificación del amplificador de potencia, de modo que la corriente de trabajo del amplificador de potencia sea moderada, lo que ahorra energía y prolonga la vida útil del amplificador de potencia (voltaje de control de alta potencia, potencia del amplificador de alta potencia).
3. Proceso de la señal de transmisión Al transmitir, la información de la banda base de transmisión (TXI-P; TXI-N; TXQ-P; TXQ-N) procesada por el circuito lógico se envía al modulador de transmisión interno de la frecuencia intermedia y se modula con la señal del oscilador local. Transmitir frecuencia intermedia. Si la estación base de la señal de FI no puede recibirla, el TX-VCO debe usarse para aumentar la frecuencia de la señal de FI a 890M-915M (GSM). Cuando TX-VCO funciona, la señal de frecuencia de 890M-915M (GSM) se genera de dos formas:
a). Se envía un muestreo al IF, mezclado con la señal del oscilador local para producir una señal de discriminación de frecuencia de transmisión igual al IF de transmisión, y se envía al detector de fase para compararlo con el IF de transmisión; si la frecuencia de oscilación del TX-VCO no coincide con la del teléfono móvil El detector de fase generará un voltaje de salto de 1-4V para controlar la capacitancia del diodo de capacitancia variable interno de TX-VCO para lograr el propósito de ajustar la frecuencia. b) El amplificador de potencia de entrada de dos vías es amplificado por la antena y convertido en ondas electromagnéticas para radiación. Para controlar la amplificación del amplificador de potencia, cuando la corriente de potencia pasa por el transformador transmisor durante la transmisión, se detecta la corriente inducida en su secundario (rectificación de alta frecuencia) y se envía al control de potencia; al mismo tiempo, la señal de nivel de potencia preestablecido también se envía a Control de potencia: después de comparar las dos señales internamente, se genera una señal de voltaje para controlar la amplificación del amplificador de potencia, de modo que la corriente de trabajo del amplificador de potencia sea moderada, lo que ahorra energía y puede extender la vida útil del amplificador de potencia. El status quo de la cadena de la industria nacional de chips de RF
En el campo de los chips de radiofrecuencia, el mercado está principalmente monopolizado por gigantes extranjeros. En términos de chips de radiofrecuencia nacionales, ninguna empresa puede respaldar de forma independiente el modo de funcionamiento de IDM, principalmente las empresas de diseño Fabless; las empresas nacionales se han formado gracias a la colaboración de diseño, fundición y embalaje. Modelo operativo "Soft IDM" ".
In terms of radio frequency chip design, domestic companies have achieved some success in 5G chips and have certain shipping capabilities. RF chip design has a high threshold. With RF development experience, it can accelerate the development of subsequent high-level RF chips.
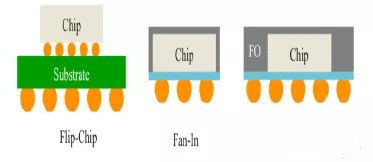
In terms of RF chip packaging, on the one hand, the increase in frequency of 5G RF chips leads to a greater impact on the circuit performance of the connection wires in the circuit. The length of the signal connection wires needs to be reduced when packaging; on the other hand, power amplifiers, low noise amplifiers, and switches are required. And the filter package becomes a module, which reduces the size on the one hand and facilitates the use of downstream terminal manufacturers on the other hand. In order to reduce the parasitics of radio frequency parameters, Flip-Chip, Fan-In and Fan-Out packaging technologies are needed.
Flip-Chip and Fan-In, Fan-Out process packaging, do not need to use gold wire bonding wire for signal connection, reducing the parasitic electrical effects caused by the gold wire bonding wire, and improving the RF performance of the chip; to the 5G era , High-performance Flip-Chip/Fan-In/Fan-Out combined with Sip packaging technology will be the future packaging trend.
Our other product: